High-Quality Vitamin A Derivative - HPR
Hydroxypinacolone retinoate(HPR) belongs to the vitamin A family and is a new generation ester of retinoic acid, formed by the esterification of retinoic acid with small molecule phenoxyethanol. Unlike other derivatives of vitamin A, HPR retains the functional group of retinoic acid, eliminating the need for conversion to retinoic acid. It can directly act on retinoic acid receptors, similar to all-trans retinoic acid, in its anti-aging effects.
A research abstract published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology (JID) compared the anti-aging and irritative effects of various forms of vitamin A in a human skin in vitro model.
 Here, they compared levels otgene transcription by HPR, ATRA, retinol (ROL), relinaldehyde (RAL), and retinyl palmitateRP) in DNA using a retinoic acid response element (RARE) reporter assay. In addition, they compared the anti-aging properties of HPR to ATRA by testing the effects on collagen levelsand skin irritation in organotypic skin models. Skin models were treated for 5 days with HPRand ATRA, basal media was collected for ELISA analysis, and skins were stained with Massonstrichrome (for collagen). RARE assay results showed that HPR had greater levels of genetranscription than ROl, RAL and RP at the same concentrations, and was less cytotoxic tocells at a 10 times higher concentration; however, HPR did not achieve gene transcriptionlevels of ATRA. Skins treated with HPR significantly increased pro-collagen production ascompared with untreated control skins, and was comparable to ATRA. Histological staining ofskins for collagen corroborated these results, with the highest dose of HPR out-performingATRA. IL-12 ELISA analysis showed that HPR did not induce more (or less) inflammatoryresponse than either ATRA or the vehicle control. Together these data suggest that HPR is aneffective alternative to ATRA and other less potent retinoids in the treatment of aging skinwithout the detrimental side effedts.
Here, they compared levels otgene transcription by HPR, ATRA, retinol (ROL), relinaldehyde (RAL), and retinyl palmitateRP) in DNA using a retinoic acid response element (RARE) reporter assay. In addition, they compared the anti-aging properties of HPR to ATRA by testing the effects on collagen levelsand skin irritation in organotypic skin models. Skin models were treated for 5 days with HPRand ATRA, basal media was collected for ELISA analysis, and skins were stained with Massonstrichrome (for collagen). RARE assay results showed that HPR had greater levels of genetranscription than ROl, RAL and RP at the same concentrations, and was less cytotoxic tocells at a 10 times higher concentration; however, HPR did not achieve gene transcriptionlevels of ATRA. Skins treated with HPR significantly increased pro-collagen production ascompared with untreated control skins, and was comparable to ATRA. Histological staining ofskins for collagen corroborated these results, with the highest dose of HPR out-performingATRA. IL-12 ELISA analysis showed that HPR did not induce more (or less) inflammatoryresponse than either ATRA or the vehicle control. Together these data suggest that HPR is aneffective alternative to ATRA and other less potent retinoids in the treatment of aging skinwithout the detrimental side effedts.

Retinol, retinaldehyde, and retinyl esters need to be converted to retinoic acid to bind to receptors and exert biological activity. The conversion process may be limited by enzyme activity, local delivery, and stability, leading to reduced or delayed activity.
HPR, on the other hand, can directly bind to retinoic acid receptors, avoiding the drawbacks of a lengthy conversion process and limitations due to enzyme activity and stability, resulting in decreased activity and delayed efficacy.
Photostability of HPR
Vitamin A structure contains five conjugated double bonds, making it highly susceptible to the energy of light waves. At 325nm, there is an absorption peak, and exposure to ultraviolet light can lead to isomerization, polymerization, and oxidation reactions, causing a loss of activity. Research has reported the impact of light on the stability of retinyl acetate (RA) and retinyl palmitate (RP). The results indicate that vitamin A esters are highly unstable in sunlight, almost completely degrading after 1 hour.
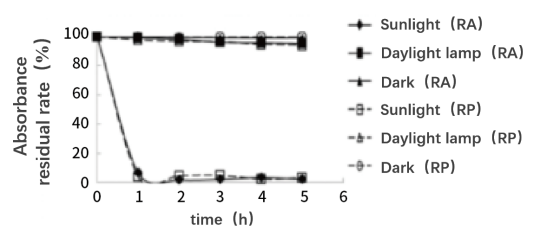
A study by Temova et al. found that light degradation of different vitamin A compounds is more pronounced than thermal degradation, with retinyl palmitate (Rpal) and β-carotene (βcal) being more prone to light degradation. After one week of exposure to light, HPR only degraded by 40%, whereas Rpal and βcal almost completely degraded. On average, among all tested vitamin A compounds, HPR exhibited the least sensitivity to light.
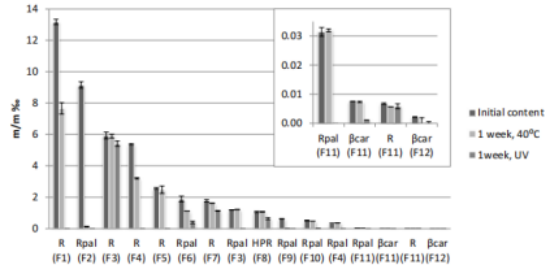
Thermal Stability of HPR
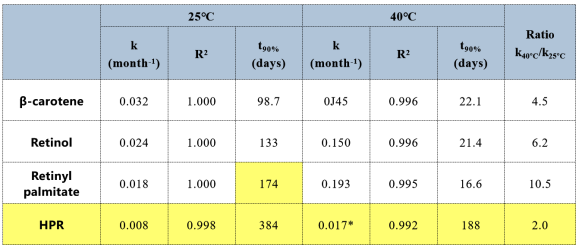
Vitamin A esters are exceptionally sensitive to temperature. Research on the thermal degradation kinetics of vitamin A esters found that the thermal degradation of vitamin A esters follows first-order kinetics (R2>0.99). Among a series of vitamin A derivatives, HPR demonstrated the optimal stability.
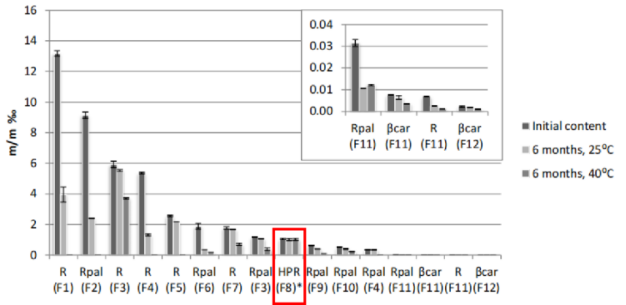
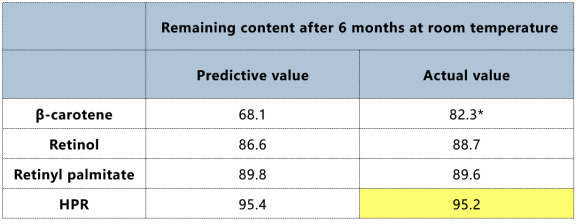
Compared to retinyl palmitate, the time required for HPR to reach 90% of its initial content extended more than twice, and after the expiration date, its measured content remained at around 95.2%. After 6 months at 25°C, HPR remained highly stable (around 95% of initial content), and even after 3 months at 40°C, its chemical stability remained excellent (content still around 97%), while other vitamin A compounds (retinol, retinyl palmitate, etc.) showed significant degradation.
Shanghai COACHCHEM Technology Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer committed to the research and production of vitamin A derivatives. We specialize in delivering premium-grade HPR(Anallerg® - HPR) in powder form, as well as a 10% HPR solution, ensuring excellence in quality and innovation.
Efficacy Stability of Anallerg® - HPR
1、Anti-aging and firming, improving skin texture
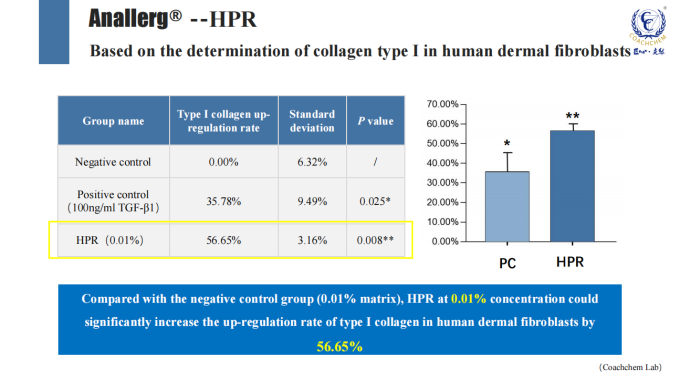
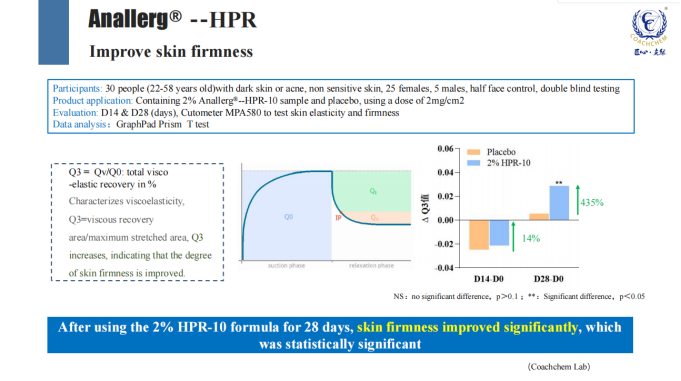
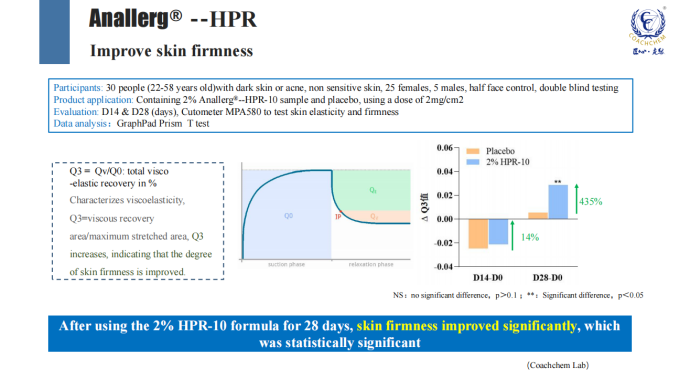
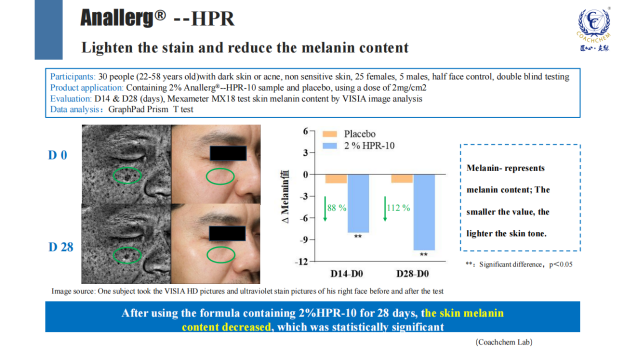
2、Lightening dark spots, reducing skin melanin
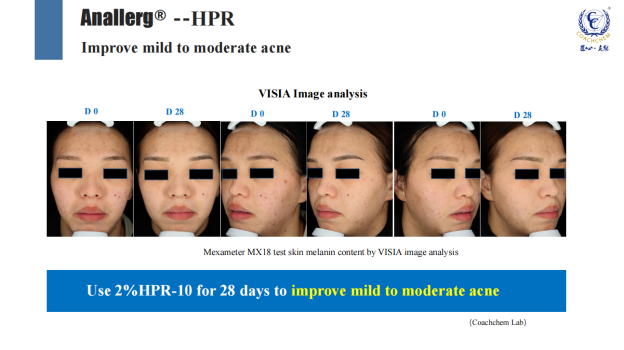
3、Acne removal, improving acne
Advantages of Anallerg® - HPR
1、High purity, high content (above 99.5%)

1、Ton-level production capacity
3、Long-term stable quality control

4、Acceptance of customization in different specifications
5、Anallerg® - HPR-10 is applied in skincare products in a solution form dissolved in the organic solvent dimethyl isosorbide (DMI), making it safer and gentler for use around the skin and eyes, enhancing the penetration of active ingredients into the epidermis.
